(183W) Tungsten NMR
Use our NMR service that provides 183W NMR and many other NMR techniques.
Tungsten (W) has one very low sensitivity NMR active nucleus, 183W (fig. 1). It is a spin ½ nucleus and yields sharp signals over a very wide chemical shift range. 183Tungsten NMR is mostly used for studying tungsten complexes, especially polyoxide clusters.
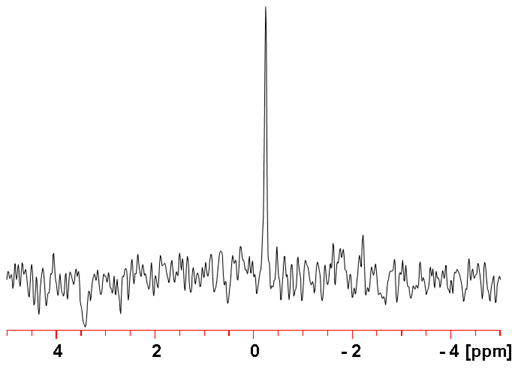
Fig. 1. 183W-NMR spectrum of Na2WO4 (1 M) in D2O
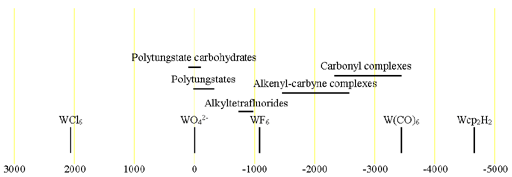
Each type of tungsten its representative chemical shift range (fig. 2).
Fig. 2. Chemical shift ranges for tungsten NMR
Tungsten shows couplings with other nuclei. One-bond couplings with fluorine are between 20 and 70 Hz. One-bond couplings to 31P are of the order of 250 Hz. With 51V, two-bond couplings of up to 26 Hz are observed. Couplings are also reported with 10B, 11B and 29Si. In polytungstates, homonuclear couplings (two-bond between 5 and 30 Hz) appear as satellite signals in the tungsten spectrum allowing the use of 2D-INADEQUATE for spectral assignment as with 13C-NMR.
Properties of 183W
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Spin | 1/2 |
| Natural abundance | 14.31% |
| Chemical shift range | 6720 ppm, from -4670 to 2050 |
| Frequency ratio (Ξ) | 4.166387% |
| Reference compound | 1 M Na2WO4 in D2O |
| Linewidth of reference | 0.6 Hz |
| T1 of reference | 5 s |
| Receptivity rel. to 1H at natural abundance | 1.07 × 10-5 |
| Receptivity rel. to 1H when enriched | 7.48 × 10-5 |
| Receptivity rel. to 13C at natural abundance | 0.0631 |
| Receptivity rel. to 13C when enriched | 0.441 |
Safety note
Some of the materials mentioned here are very dangerous. Ask a qualified chemist for advice before handling them. Qualified chemists should check the relevant safety literature before handling or giving advice about unfamiliar substances. NMR solvents are toxic and most are flammable. Specifically, tungsten salts are toxic: wear protective gloves.
References
- W. McFarlane, A. M. Noble and J. M Winfield, "Reversal of the sign of the tungsten-183-fluorine-19 spin-spin coupling constant in octahedral tungsten (VI) derivatives" Chem. Phys. Lett., 6, 547-548 (1970).
- F. H. Koehler, H. J. Kalder and E. O. Fischer, "Carbon-13-tungsten-183 coupling as a probe for metal-carbyne, -carbene, and -alkyl compounds", J. Organometal. Chem., 85, C19-C22 (1975).
- J. Banck and A. Schwenk, "Tungsten-183 NMR studies", Z. Phys. B, 20, 75-80 (1975).
- R. Acerete, C. F. Hammer and L. C. W. Baker, "Direct tungsten-183 nuclear magnetic resonance: a powerful new structural tool for heteropoly- and isopolytungstate chemistry", J. Am. Chem. Soc., 101, 267-269 (1979).
- M. A. Fedotov, L. P. Kazanskii and V. I. Spitsyn, "Oxygen-17 and tungsten-183 NMR chemical shifts in polyoxotungstates and the lengths of tungsten -oxygen bonds", Dokl. Akad. Nauk SSSR, 272, 1179-1185 (1983).
- P. J. Domaille, "The 1- and 2-dimensional tungsten-183 and vanadium-51 NMR characterization of isopolymetalates and heteropolymetalates", J. Am. Chem. Soc., 106, 7677-7687 (1984).
- Y. Ma, P. Demou and J. W. Faller, "A tungsten-183 NMR study of mononuclear tungsten (VI) methyl complexes containing terminal oxo, sulfido, and imido ligands", Inorg. Chem., 30, 62-64 (1991).
- J.-F. Liu, W.-Q. Wang, L. Meng and Y. Liu, "183W NMR characterization of rare earth heteropolymetalates in aqueous solution", Gaodeng Xuexiao Huaxue Xuebao, 17, 179-182 (1996).
- L. Zhang, M. P. Gamasa, J. Gimeno, R. J. Carbajo, F. Lopez-Ortiz, M. Lanfranchi and A. Tiripicchio, "Synthesis and Characterization of Tungsten Alkenyl-Carbyne Complexes [cyclic] trans-[(dppe)(CO)2LW≡CCH:CCH2(CH2)nCH2CH2][BF4] (L = CO, MeCN, PMe3) and [cyclic] [(dppe)(CO)2XW≡CCH:CCH2(CH2)nCH2CH2] (X = Cl, Br, I). X-ray Crystal Structure of [(dppe)(CO)2ClW≡CCH:CCH2CH2)nCH2CH2] and 183W NMR Studies", Organometal., 15, 4274-4284 (1996).
- S. Chapelle, P. Koll, Peter and J.-F. Verchere, "A multinuclear NMR spectroscopy characterization of dinuclear tungsten (VI) complexes of tridentate and pentadentate meso-D-glycero-D-gulo-heptitol and D-glycero-L-gulo-heptitol", Carbohydr. Res., 306, 27-34 (1998).
- R. J. Carbajo, L. Zhang, Lei and F. Lopez-Ortiz, "183W NMR study of alkenylcarbyne- and alkenylvinylidene- tungsten complexes", Magn. Reson. Chem., 36, 807-814 (1998).
- Y. Chen, L. Qu, Lunyu and J. He, "Application of 183W NMR technique in the study of polyoxometalates", Huaxue Tongbao, 65, w53/1-w53/6 (2002).
- B. J. Smith and V. A. Patrick, "Tungsten NMR spectra of the α- and β-isomers of Na8[SiW11O39]", Aust. J. Chem., 56, 283-286 (2003).
- I. Kawafune, "183W NMR spectral behavior of A-type metal-trisubstituted dodecatungstophosphate anion salts", Kagaku to Kogyo, 77, 452-458 (2003).
- G. Lenoble, B. Hasenknopf and R. Thouvenot, "A Strategy for the Analysis of Chiral Polyoxotungstates by Multinuclear (31P, 183W) NMR Spectroscopy Applied to the Assignment of the 183W NMR Spectra of a 1-[P2W17O61]10- and a 1-[YbP2W17O61]7-", J. Am. Chem. Soc., 128, 5735-5744 (2006).