Attached proton test (APT)
The attached proton test is a 1D 13C NMR experiment that is used as an aid to assignment by separating carbons unattached to protons and CH2 signals from CH and CH3 signals. The APT experiment yields methine (CH) and methyl (CH3) signals positive and quaternary (C) and methylene (CH2) signals negative. It is slightly less sensitive than DEPT but a single experiment shows all carbon signals at once unlike DEPT that supresses quaternary carbons and requires up to three different acquisitions to yield full results. Fig. 1 shows the APT spectrum of ethylbenzene.
Fig. 1. APT spectrum of ethylbenzene showing CH and CH3 positive while CH2 and quaternary C are negative

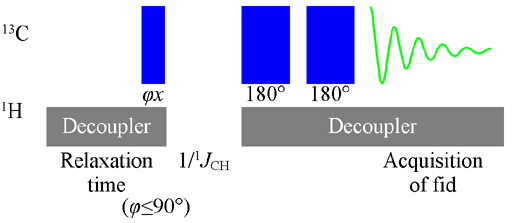
The APT pulse sequence is shown in fig. 2. The delay between the first two pulses is set to one over the carbon proton coupling constant. For CH2 (which is the deciding factor for this experiment) this is usually about 125 Hz so the delay is 8 ms. Between the last two pulses and between the last pulse and the acquisition 100μs is usually sufficient.
Fig. 2. Pulse sequence for APT