(Rb) Rubidium NMR
Use our NMR service that provides Rb NMR and many other NMR techniques.
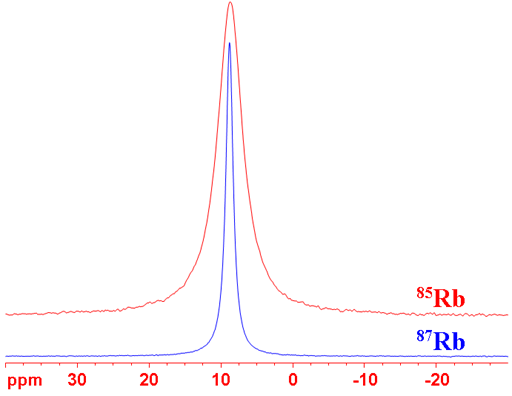
Rubidium (Rb) has two NMR active nuclei, 85Rb and 87Rb, that are both quadrupolar and yield broad to very broad lines over a wide chemical shift range. 87Rb is preferred as it has the highest sensitivity and yields less broad signals than 85Rb (fig. 1). Rubidium NMR is mostly used for detecting binding in aqueous solutions as a substitute for the less NMR sensitive potassium cation by measuring its relaxation rate.
Fig. 1. Comparison of the rubidium isotopes under comparable conditions for RbCl (1M) in D2O
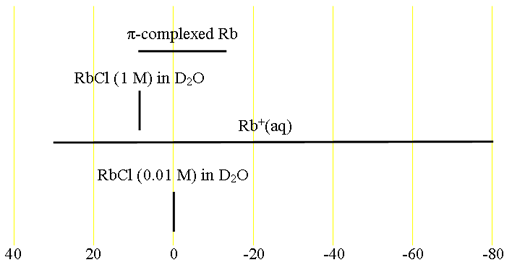
Both the isotopes have the same chemical shifts (fig. 2) although there is little information available about these shifts.
Fig. 2. Chemical shift ranges for rubidium NMR
85Rubidium NMR
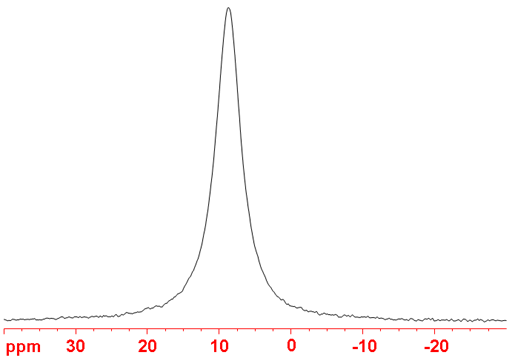
(85Rb) 85Rubidium (fig. 3) is a spin 5/2 nucleus and is therefore quadrupolar. As a result, the signal width increases with asymmetry of the environment. It is less sensitive and yields broader signals than 87Rb so 85Rb is not the nucleus of choice for rubidium NMR unless studying isotopic enrichment.
Fig. 3. 85Rb-NMR spectrum of RbCl (1M) in D2O
Properties of 85Rb
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Spin | 5/2 |
| Natural abundance | 72.17% |
| Chemical shift range | 110 ppm, from -80 to 30 |
| Frequency ratio (Ξ) | 9.654943% |
| Reference compound | 0.01 M RbCl in D2O |
| Linewidth of reference | 152 Hz |
| T1 of reference | 0.00185 s |
| Receptivity rel. to 1H at natural abundance | 7.67 × 10-3 |
| Receptivity rel. to 1H when enriched | 0.0106 |
| Receptivity rel. to 13C at natural abundance | 45.0 |
| Receptivity rel. to 13C when enriched | 62.4 |
| Linewidth parameter | 240 fm4 |
87Rubidium NMR
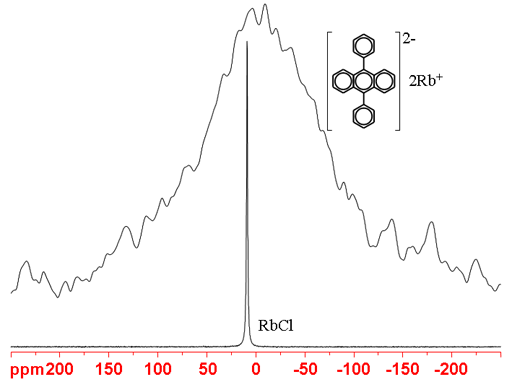
(87Rb) 87Rubidium is a spin 3/2 nucleus and is therefore quadrupolar. As a result, the signal width increases with asymmetry of the environment. 87Rb is more sensitive and yields narrower lines than 85Rb so is the rubidium nucleus of choice. In fig. 4, the RbCl signal is much narrower than that of rubidium diphenylanthracene.
Fig. 4. 87Rb-NMR spectra of RbCl (1M) in D2O and rubidium diphenylanthracene
Properties of 87Rb
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Spin | 3/2 |
| Natural abundance | 27.83% |
| Chemical shift range | 110 ppm, from -80 to 30 |
| Frequency ratio (Ξ) | 32.720454% |
| Reference compound | 0.01 M RbCl in D2O |
| Linewidth of reference | 149 Hz |
| T1 of reference | 0.005 s |
| Receptivity rel. to 1H at natural abundance | 0.0493 |
| Receptivity rel. to 1H when enriched | 0.177 |
| Receptivity rel. to 13C at natural abundance | 290 |
| Receptivity rel. to 13C when enriched | 1042 |
| Linewidth parameter | 83 fm4 |
Safety note
Some of the materials mentioned here are very dangerous. Ask a qualified chemist for advice before handling them. Qualified chemists should check the relevant safety literature before handling or giving advice about unfamiliar substances. NMR solvents are toxic and most are flammable. Specifically, rubidium salts are toxic in very large doses. This is besides any toxicity that may arise from the anion. 87Rb is very slightly radioactive, but is unlikely to pose a radiation hazard.
References
- B. Lindman and I. Lindqvist, "Nuclear quadrupole relaxation of rubidium-85 in an aqueous solution of a humic acid", Acta Chem. Scand., 23, 2215-2216 (1969).
- Z. H. Endre, J. L. Allis, P. J. Ratcliffe and G. K. Radd, "87-rubidium NMR : a novel method of measuring cation flux in intact kidney" Kidney international, 35, 1249-1256 (1989).
- O. Jilkina, B. Xiang, B. Kuzio, J. Rendell and V. V. Kupriyanov, "Potassium transport in langendorff-perfused mouse hearts assessed by 87Rb NMR spectroscopy" Magn. Reson. Med., 53, 1172-1176 (2005).