(73Ge) Germanium NMR
Use our NMR service that provides 73Ge NMR and many other NMR techniques.
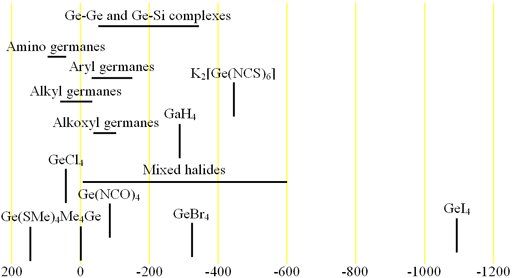
73Germanium (73Ge) is the only NMR active nucleus of germanium. It is a low sensitivity nucleus that yields moderately broad lines (fig. 1) in symmetric environments over a very wide chemical shift range. For larger complexes and molecules, the signals become too broad to observe with a high-resolution NMR spectrometer. 73Ge NMR is used for studying small complexes of germanium and for relaxation studies of germanium binding. Each type of germanium has its own chemical shift range (fig. 2).
Fig. 1. 73Ge-NMR spectrum of neat GeCl4
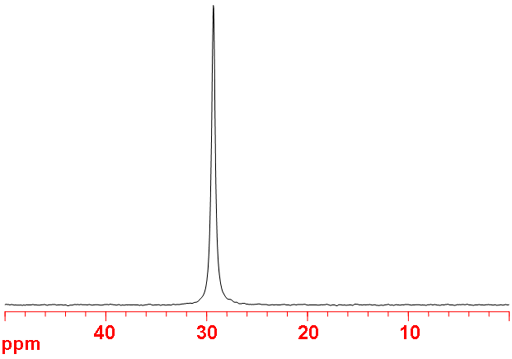
Fig. 2. Chemical shift ranges for germanium NMR
73Ge often displays heteronuclear spin-spin couplings. One-bond couplings to 1H are typically 88 to 98 Hz, two-bond are approximately 3 Hz and three-bond are approximately -2 Hz. One-bond couplings to flourine are dependent on coordination number: four yields 178 Hz while six yields 98 Hz. The coupling to 13C in (CH3)4Ge has been measured to be -18.7 Hz.
Properties of 73Ge
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Spin | 9/2 |
| Natural abundance | 7.73% |
| Chemical shift range | 1261 ppm, from -1108 to 153 |
| Frequency ratio (Ξ) | 3.488315% |
| Reference compound | neat (CH3)4Ge |
| Linewidth of reference | 0.5 Hz |
| T1 of reference | 0.295 s |
| Receptivity rel. to 1H at natural abundance | 1.09 × 10-4 |
| Receptivity rel. to 1H when enriched | 1.41 × 10-3 |
| Receptivity rel. to 13C at natural abundance | 0.642 |
| Receptivity rel. to 13C when enriched | 8.31 |
| Linewidth parameter | 28 fm4 |
Safety note
Some of the materials mentioned here are very dangerous. Ask a qualified chemist for advice before handling them. Qualified chemists should check the relevant safety literature before handling or giving advice about unfamiliar substances. NMR solvents are toxic and most are flammable. Specifically, GeCl4 and other tetrahalids are corrosive, poisonous and react violently with water and moist air. Organogermanes are poisonous and flammable.
References
- J. Kaufmann, W. Sahm and A. Schwenk, "Germanium-73 nuclear magnetic resonance studies" Z. Naturfors. A, 26, 1384-9 (1971).
- E. Kupce, E. Upena, M. Trusule and E. Lukevics, "Germanium-73 NMR spectroscopy of aminogermanes" Latvijas PSR Zinatnu Akademijas Vestis, Kimijas Serija, (3), 359-60 (1988).
- E. Liepiņš, I. Zicmane, E. Lukevics, "Germanium-73 NMR spectroscopic studies of organogermanium compounds" J. Organometal. Chem., 341, 315-33 (1988).
- E. Liepiņš, I. Zicmane, L. M. Ignatovich and E. Lukevics, "Germanium-73 NMR spectra of 2-thienyl-, 2-furyl- and 2-(4,5-dihydrofuryl)germanes" J. Organometal. Chem., 389, 23-8 (1990).
- E. Liepiņš, M. V. Petrova, E. T. Bogoradovskii and V. S. Zavgorodnii, "Germanium-73, carbon-13 and proton NMR spectra of methylethynylgermanes" J. Organometal. Chem., 410, 287-91 (1991).
- Y. Takeuchi and T. Takayama, Toshio. "73Ge NMR spectroscopy of organogermanium compounds" Ann. Rep. NMR Spectrosc., 5, 155-200 (2005)