(In) Indium NMR
Use our NMR service that provides In NMR and many other NMR techniques.
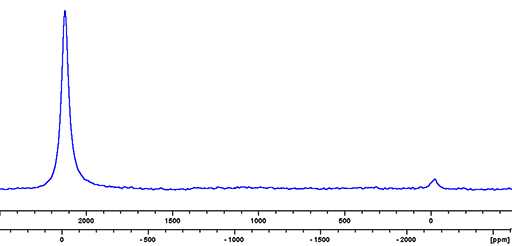
Indium (In) has two NMR active nuclei that have a very wide chemical shift range. 113In and 115In, are both quadrupolar and yield extremely broad lines even in small symmetrical ions. 115In is preferred as it has the higher sensitivity and yields very slightly narrower signals than 113In (fig. 1). Indium NMR has limited use used for the study of solvated indium ions or molten salts. Indium is unusual in that their resonant frequency difference is a little over 2000 ppm so both nuclei can be observed at the same time (fig. 1).
Fig. 1. Comparison of the indium isotopes 113In on the right (upper scale) and 115In on the left (lower scale) for In(NO3)3 in nitric acid/D2O
Both the isotopes have the same chemical shifts (fig. 2).
Fig. 2. Chemical shift ranges for indium NMR
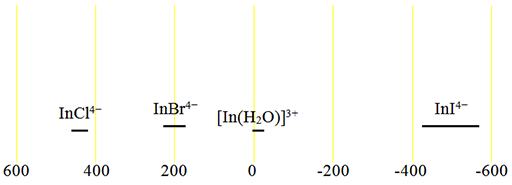
113Indium NMR
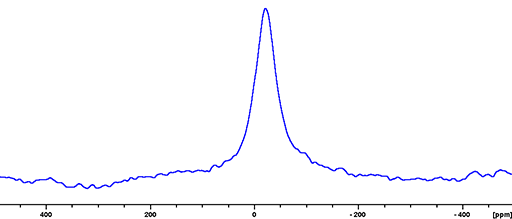
(113In) 113Indium is a spin 9/2 nucleus and is therefore quadrupolar. As a result, the signal width is very broad for small symmetrical ions and increases with asymmetry of the environment (fig. 3). 113In is less sensitive and yields marginally broader signals than 115In so 115In is the nucleus of choice for indium NMR unless studying isotopic enrichment.
Fig. 3. 113In-NMR spectrum of In(NO3)3 in nitric acid/D2O
Properties of 113In
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Spin | 9/2 |
| Natural abundance | 4.29% |
| Chemical shift range | 1100 ppm, from -500 to 600 |
| Frequency ratio (Ξ) | 21.865755% |
| Reference compound | In(NO3)3 (0.1 M) in dilute HNO3 |
| Linewidth of reference | 4314 Hz |
| T1 of reference | 50 µs |
| Receptivity rel. to 1H at natural abundance | 0.0151 |
| Receptivity rel. to 1H when enriched | 0.352 |
| Receptivity rel. to 13C at natural abundance | 88.5 |
| Receptivity rel. to 13C when enriched | 2063 |
| Linewidth parameter | 470 fm4 |
115Indium NMR
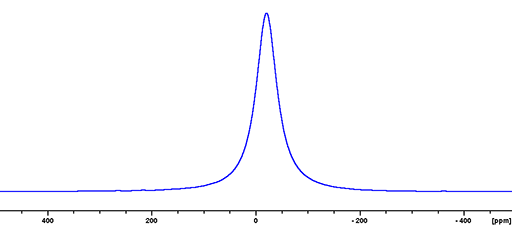
(115In) 115Indium is a spin 9/2 nucleus and is therefore quadrupolar. As a result, the signal width is very broad for small symmetrical ions and increases with asymmetry of the environment (fig. 4). 115In is more sensitive and yields marginally less broad lines than 113In so 115In is the indium nucleus of choice.
Fig. 4. 115In-NMR spectrum of In(NO3)3 in nitric acid/D2O
Properties of 115In
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Spin | 9/2 |
| Natural abundance | 95.71% |
| Chemical shift range | 1100 ppm, from -500 to 600 |
| Frequency ratio (Ξ) | 21.912629% |
| Reference compound | In(NO3)3 (0.1 M) in dilute HNO3 |
| Linewidth of reference | 4263 Hz |
| T1 of reference | 50 µs |
| Receptivity rel. to 1H at natural abundance | 0.338 |
| Receptivity rel. to 1H when enriched | 0.353 |
| Receptivity rel. to 13C at natural abundance | 1980 |
| Receptivity rel. to 13C when enriched | 2069 |
| Linewidth parameter | 490 fm4 |
Safety note
Some of the materials mentioned here are very dangerous. Ask a qualified chemist for advice before handling them. Qualified chemists should check the relevant safety literature before handling or giving advice about unfamiliar substances. NMR solvents are toxic and most are flammable. Specifically, indium salts may be toxic.