(127I) Iodine NMR
Use our NMR service that provides 127I NMR and many other NMR techniques.
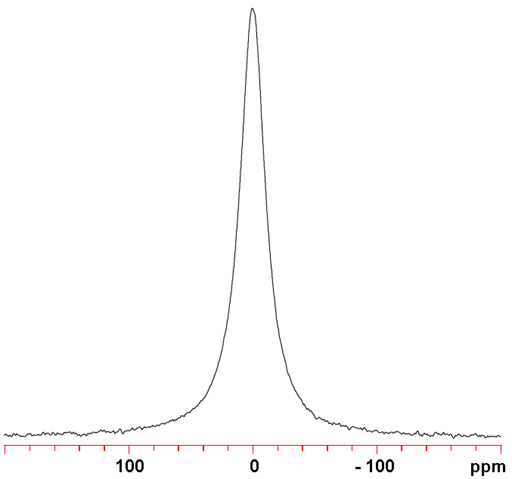
Iodine (I) has one NMR active nucleus, 127I with a very wide chemical shift range. The nucleus is of medium to high sensitivity but is quadrupolar and yields very broad signals as ions in symmetrical environments (fig. 1) and signals, too broad to be observed with a high-resolution NMR spectrometer, even in ionic clusters and small molecules. The relaxation time of the I4- ion has been measured to be 110 ns, corresponding to a line-width of 6 MHz, much too wide to be observed with a high-resolution NMR spectrometer. As a result, 127I NMR is restricted to relaxation studies of the binding of iodide ions.
Fig. 1. 127I-NMR spectrum of KI (1 M) in D2O
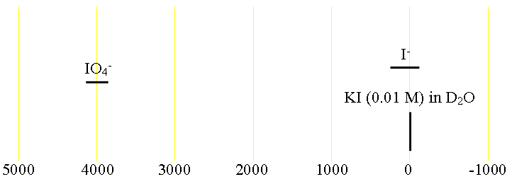
There is very little information about iodine chemical shifts (fig. 2).
Fig. 2. Chemical shift ranges for iodine NMR
Properties of 127I
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Spin | 5/2 |
| Natural abundance | 100% |
| Chemical shift range | 4200 ppm, from -100 to 4100 |
| Frequency ratio (Ξ) | 20.007486% |
| Reference compound | KI (0.01 M) in D2O |
| Linewidth of reference | 1926 Hz |
| T1 of reference | 0.000135 s |
| Receptivity rel. to 1H at natural abundance | 0.0954 |
| Receptivity rel. to 1H when enriched | 0.0954 |
| Receptivity rel. to 13C at natural abundance | 560 |
| Receptivity rel. to 13C when enriched | 560 |
| Linewidth parameter | 1600 fm4 |
Safety note
Some of the materials mentioned here are very dangerous. Ask a qualified chemist for advice before handling them. Qualified chemists should check the relevant safety literature before handling or giving advice about unfamiliar substances. NMR solvents are toxic and most are flammable. Specifically, iodide is toxic in large doses. Other oxidation states are more toxic: wear protective gloves.
References
- C. Hall, "Application of chlorine, bromine, and iodine NMR spectroscopy to the study of physicochemical processes in liquids", Q. Rev., Chem. Soc., 25, 87-109 (1971).
- "NMR, Basic Principles and Progress, Vol. 12: Chlorine, Bromine and Iodine NMR. Physico-Chemical and Biological Applications", P. Diehl, E. Fluck, and R. Kosfeld, Eds., Springer Verlag, 368 pp. (1976).
- T. Drakenberg and S. Forsen, "[NMR of] the halogens - chlorine, bromine, and iodine" NATO ASI Series, Series C: Mathematical and Physical Sciences 103 (Multinucl. Approach NMR Spectrosc.), 405-44 (1983).