(67Zn) Zinc NMR
Use our NMR service that provides 67Zn NMR and many other NMR techniques.
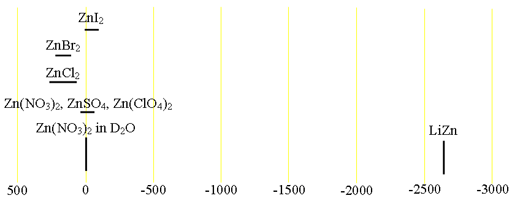
67Zinc (67Zn) is the only NMR active nucleus of zinc. It is a low sensitivity nucleus that yields moderately broad lines in symmetric environments over a very wide chemical shift range (fig. 1). For larger complexes and molecules, the signals become too broad to observe with a high-resolution NMR spectrometer. 67Zn NMR is used for studying small complexes of zinc and for relaxation studies of zinc binding. There is little information available about chemical shifts (fig. 2).
Fig. 1. 67Zn-NMR spectrum of ZnClO4 (1M) in D2O
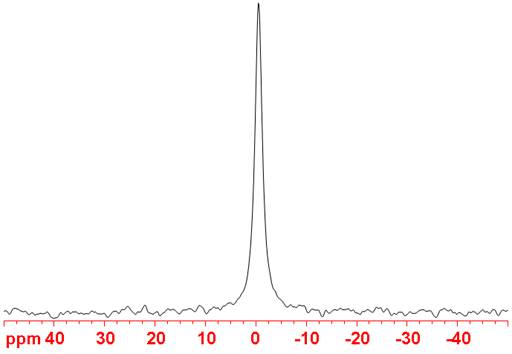
Fig. 2. Chemical shift ranges for zinc NMR
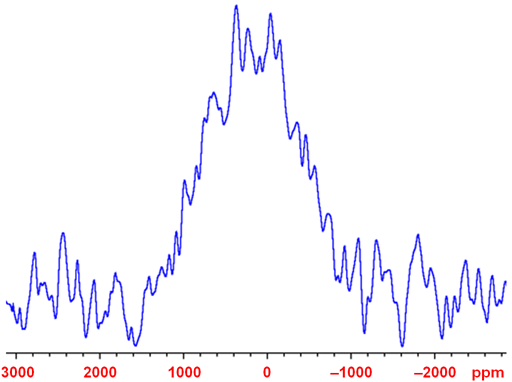
Many NMR probes contain zinc that can cause a background signal to be observed (fig. 3).
Fig. 3. Background 67Zn-NMR signal arising from zinc in the probe
Properties of 67Zn
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Spin | 5/2 |
| Natural abundance | 4.10% |
| Chemical shift range | 2700 ppm, from 0 to -2700 |
| Frequency ratio (Ξ) | 6.256803%% |
| Reference compound | sat. Zn(NO3)2 in D2O |
| Linewidth of reference | 25 Hz |
| T1 of reference | 0.015 s |
| Receptivity rel. to 1H at natural abundance | 1.18 × 10-4 |
| Receptivity rel. to 1H when enriched | 2.88 × 10-3 |
| Receptivity rel. to 13C at natural abundance | 0.692 |
| Receptivity rel. to 13C when enriched | 16.9 |
| Linewidth parameter | 72 fm4 |
References
- B. W. Epperlein, H. Krueger, O. Lutz, A. Schwenk, "Fourier transform nuclear magnetic resonance studies of zinc-67" Z. Naturforschung A., 29, 1533-1557 (1974).
- G. E. Maciel, L. Simeral, J. J. H. Ackerman, "Effect of Complexation of Zinc(II) on Zinc-67 Chemical Shifts" J. Phys. Chem., 81, 263-267 (1977).
Safety note
Some of the materials mentioned here are very dangerous. Ask a qualified chemist for advice before handling them. Qualified chemists should check the relevant safety literature before handling or giving advice about unfamiliar substances. NMR solvents are toxic and most are flammable. Specifically, ZnClO4 is toxic: wear gloves. Zinc salts are toxic in very high doses.