(59Co) Cobalt NMR
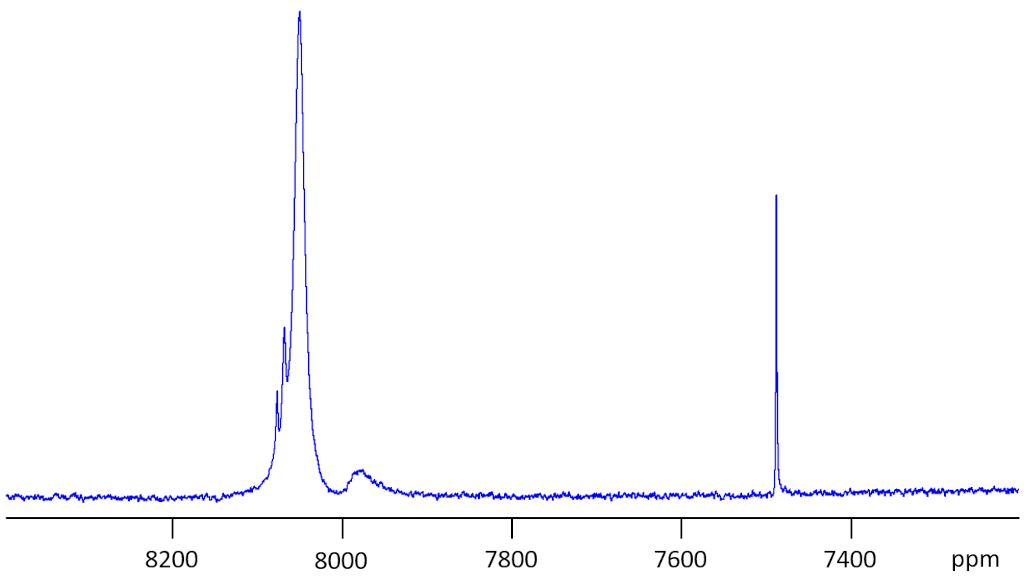
59Cobalt (59Co) is a high sensitivity nucleus with a 100% natural abundance that yields somewhat broad lines even in symmetric environments and very broad lines for slightly larger complexes over an extremely wide chemical shift range. 59Co is a spin 7/2 nucleus and is therefore quadrupolar. As a result, the signal width increases with asymmetry of the environment. The most common oxidation state of cobalt salts is Co(II). However, this is paramagnetic so cannot be observed on a high resolution NMR spectrometer. 59Co NMR is observable for Co(III), Co(I) and some clusters that are formally Co(0) or Co(-I). 59Co NMR is used for studying small Co complexes. Each type of cobalt compound has its characteristic chemical shift (fig. 1). A 59Co spectrum of acqueous Na3Co(NO2)6 is shown in fig. 2. The sample shows extra signals due to partial hydrolysis.
Fig. 1. Chemical shift ranges for cobalt NMR
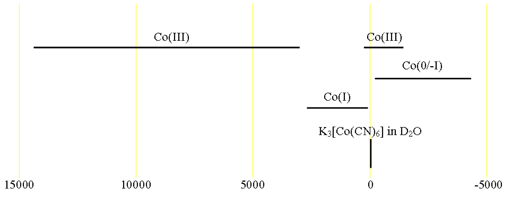
Fig. 2. 59Co spectrum Na3Co(NO2)6 in D2O
Please ask us for 59Co-NMR service.
Properties of 59Co
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Spin | 7/2 |
| Natural abundance | 100% |
| Chemical shift range | 18000 ppm, from -4000 to 14000 |
| Frequency ratio (Ξ) | 23.727074% |
| Reference compound | 0.56 m K3[Co(CN)6] in D2O |
| Linewidth of reference | 5 Hz |
| T1 of reference | 0.1 s |
| Receptivity rel. to 1H at natural abundance | 0.278 |
| Receptivity rel. to 1H when enriched | 0.278 |
| Receptivity rel. to 13C at natural abundance | 1640 |
| Receptivity rel. to 13C when enriched | 1640 |
| Linewidth parameter | 240 fm4 |
References
- S. C. F. Au-Yeung and D. R. Eaton, "The Solvent and Field Dependence of 59Co NMR Linewidths", J. Magn. Reson., 52, 366-373 (1983).
- T. Richert, K. Elbayed, J. Raya, P. Granger, P. Braunstein and J. Rosé, "59Co NMR in Tetrahedron Clusters", Magn. Reson. Chem., 34, 689-696 (1996).
Safety note
Some of the materials mentioned here are very dangerous. Ask a qualified chemist for advice before handling them. Qualified chemists should check the relevant safety literature before handling or giving advice about unfamiliar substances. NMR solvents are toxic and most are flammable. Specifically, cobalt salts are toxic.