(43Ca) Calcium NMR
Use our NMR service that provides 43Ca NMR and many other NMR techniques.
43Calcium (43Ca) is a moderately sensitivity nucleus but with a very low natural abundance that yields moderately sharp lines (fig. 1) in symmetric environments over a small chemical shift range. 43Ca is a spin 7/2 nucleus and is therefore quadrupolar. As a result, the signal width increases with asymmetry of the environment. 43Ca NMR is mostly used in relaxation studies to determine binding to DNA, proteins, etc. Because of its extremely low sensitivity at natural abundance, it is usually isotopically enriched for these studies despite the cost. There is little information available about chemical shifts (fig. 2).
Fig. 1. 43Ca-NMR spectrum of CaCl2 (1M) in D2O
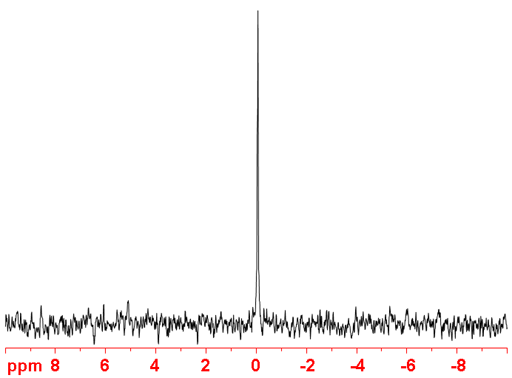
Fig. 2. Chemical shift ranges for calcium NMR
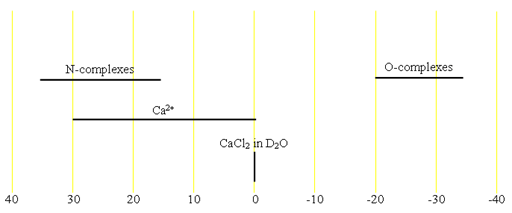
Properties of 43Ca
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Spin | 7/2 |
| Natural abundance | 0.135% |
| Chemical shift range | 70 ppm, from -35 to 35 |
| Frequency ratio (Ξ) | 6.730029% |
| Reference compound | 0.1 M CaCl2 in D2O |
| Linewidth of reference | 0.5 Hz |
| T1 of reference | 1 s |
| Receptivity rel. to 1H at natural abundance | 8.68 × 10-6 |
| Receptivity rel. to 1H when enriched | 6.42 × 10-3 |
| Receptivity rel. to 13C at natural abundance | 0.051 |
| Receptivity rel. to 13C when enriched | 37.8 |
| Linewidth parameter | 2.3 fm4 |
Safety note
Some of the materials mentioned here are very dangerous. Ask a qualified chemist for advice before handling them. Qualified chemists should check the relevant safety literature before handling or giving advice about unfamiliar substances. NMR solvents are toxic and most are flammable. Specifically, calcium salts are non-toxic on account of their calcium under normal circumstances. However, their anions may be toxic.