(Cl) Chlorine NMR
Use our NMR service that provides Cl NMR and many other NMR techniques.
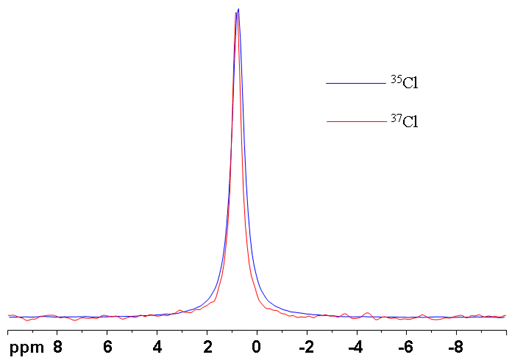
(Cl) Chlorine has two useful NMR active nuclei 35Cl and 37Cl. Both yield relatively broad signals but have a broad chemical shift range. 35Cl is more sensitive but 37Cl yields slightly higher resolution (fig. 1). In most cases, the extra sensitivity of 35Cl is more important than the extra resolution of 37Cl. Either nucleus can be used to detect and quantify the presence of ionic chlorides. Organic chlorides yield very broad signals of the order of tens of kHz so Cl NMR is of limited to the smallest for organic chlorides.
Fig. 1. Comparison of 35Cl and 37Cl NMR of NaCl solution showing that 37Cl yields slightly sharper signals at the expense of a significant reduction in sensitivity
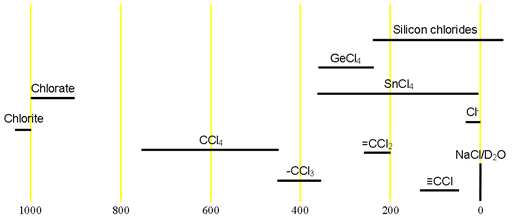
The main use of chlorine NMR is for very small organic and inorganic molecules and the study of chloride binding. Each type of compound has its characterictic chemical shift range (fig. 2).
Fig. 2. Chemical shift ranges for chlorine NMR
35Chlorine NMR
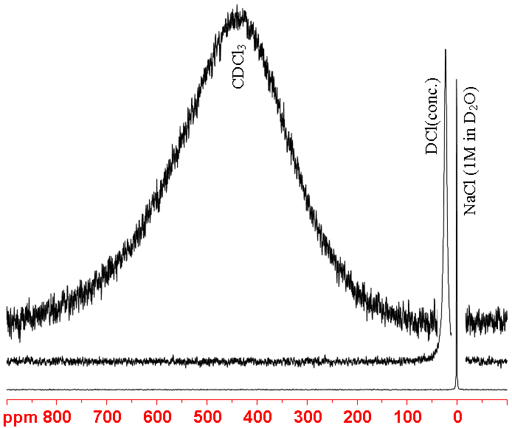
35Cl NMR is significantly more sensitive than 37Cl NMR and although it yields slightly broader signals it is usually preferred over 37Cl. 35Cl is a spin 3/2 quadrupolar nucleus and its signals become broader with increasing molecular size and asymmetry (fig. 3). 35Cl can be used to study ionic and inorganic chlorides. Organic chlorides yield very broad signals of the order of tens of kHz so 35Cl NMR is of limited to the smallest for organic chlorides.
Fig. 3. 35Cl-NMR spectra showing increasing linewidth with increasing environmental asymmetry
Properties of 35Cl
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Spin | 3/2 |
| Natural abundance | 75.78% |
| Chemical shift range | 1100 ppm, from -50 to 1050 |
| Frequency ratio (Ξ) | 9.797909% |
| Reference compound | 0.1 M NaCl in D2O |
| Linewidth of reference | 11.4 Hz |
| T1 of reference | 0.04 s |
| Receptivity rel. to 1H at natural abundance | 3.58 × 10-3 |
| Receptivity rel. to 1H when enriched | 4.72 × 10-3 |
| Receptivity rel. to 13C at natural abundance | 21.0 |
| Receptivity rel. to 13C when enriched | 27.7 |
| Linewidth parameter | 89 fm4 |
37Chlorine NMR
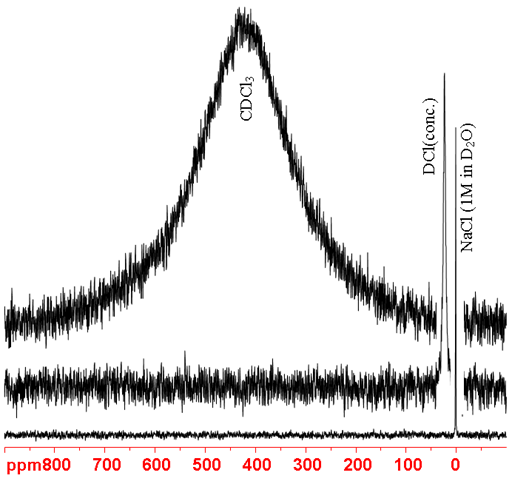
37Cl NMR yields slightly narrower signals than 35Cl NMR. However, because it is significantly less sensitive 35Cl is usually preferred over it. 37Cl is a spin 3/2 quadrupolar nucleus and its signals become broader with increasing molecular size and asymmetry (fig. 4). 37Cl can be used to study ionic and inorganic chlorides. Organic chlorides yield very broad signals of the order of tens of kHz so 37Cl NMR is of limited to the smallest for organic chlorides.
Fig. 4. 37Cl-NMR spectra showing increasing linewidth with increasing environmental asymmetry
Properties of 37Cl
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Spin | 3/2 |
| Natural abundance | 24.22% |
| Chemical shift range | 1100 ppm, from -50 to 1050 |
| Frequency ratio (Ξ) | 8.155725% |
| Reference compound | 0.1 M NaCl in D2O |
| Linewidth of reference | 7.5 Hz |
| T1 of reference | 0.06 s |
| Receptivity rel. to 1H at natural abundance | 6.59 × 10-4 |
| Receptivity rel. to 1H when enriched | 2.72 × 10-3 |
| Receptivity rel. to 13C at natural abundance | 3.87 |
| Receptivity rel. to 13C when enriched | 16.0 |
| Linewidth parameter | 55 fm4 |
Safety note
Some of the materials mentioned here are very dangerous. Ask a qualified chemist for advice before handling them. Qualified chemists should check the relevant safety literature before handling or giving advice about unfamiliar substances. NMR solvents are toxic and most are flammable. Specifically, chloride is non-toxic under normal conditions, however, other oxidation states of chlorine, and organic chlorides are toxic and may be carcinogens, hydrochloric acid is corrosive and toxic: wear protective gloves and, if volatile, work in a hood.