(103Rh) Rhodium NMR
Use our NMR service that provides 103Rh NMR and many other NMR techniques.
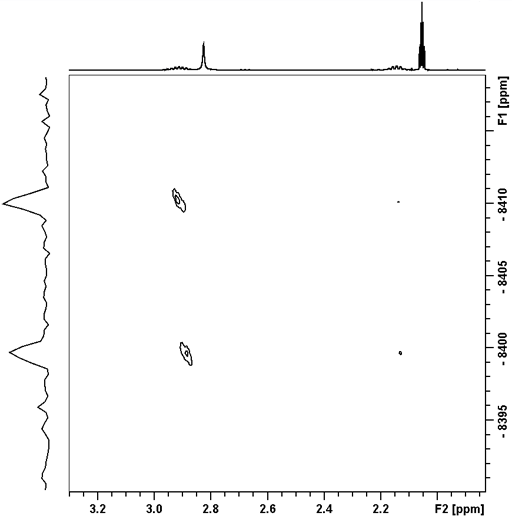
Rhodium (Rh) has one NMR active nucleus, 103Rh with an extremely wide chemical shift range. The nucleus is spin ½ and gives very sharp signals but has very low sensitivity (fig. 1). 103Rh-NMR is usually observed indirectly via protons using heteronuclear correlation (fig. 2).
Fig. 1. 103Rh-NMR spectrum of a dirhodium complex showing coupling to 31P
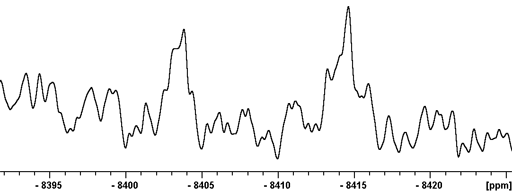
Fig. 2. Indirect detection of 103Rh using 2D HMQC for a dirhodium complex showing coupling to 31P
Each type of rhodium has its chemical shift range (fig. 3).
Fig. 3. Chemical shift ranges for rhodium NMR showing the IUPAC and a commonly used alternative scale
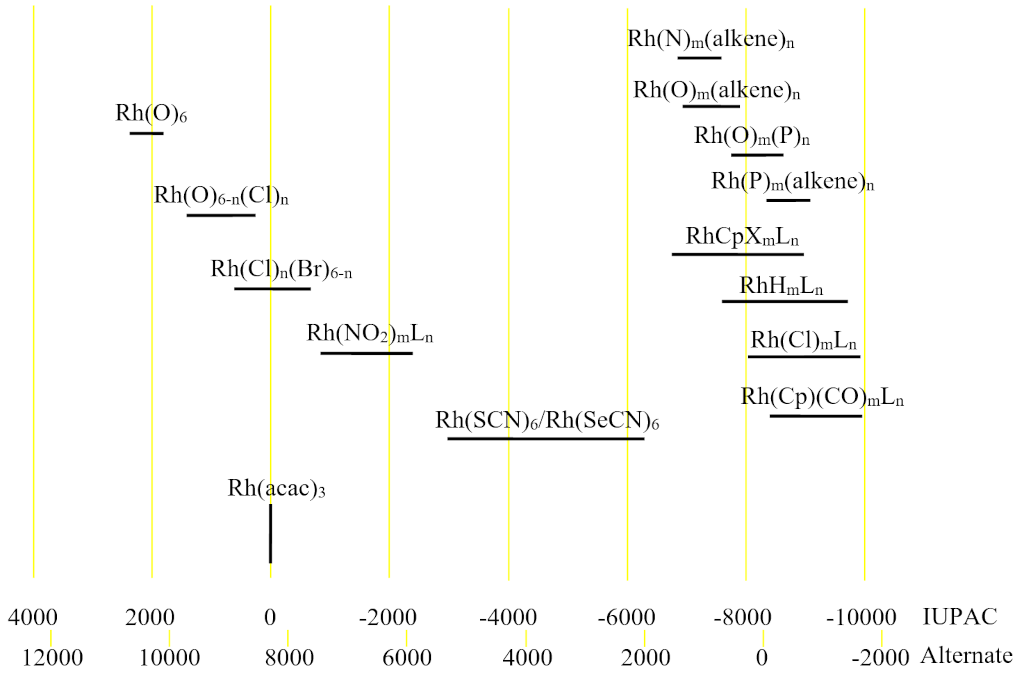
103Rh-NMR is used for the study of rhodium complexes that are widely used as catalysts in research and industry. The extremely wide chemical shift range means that the rhodium chemical shift varies greatly with isomer, solvent and concentration. Many rhodium complexes display dynamic behavior that can be studied and quantified by NMR.
Rhodium often shows couplings to other nuclei, 1H, 13C, 31P, etc. One bond couplings to 31P depend on many factors (such as oxidation state, steric hindrance and coordination number) and vary from 20 to 375 Hz. One bond couplings to 15N are usualy around 24 Hz and to 13C between 15 and 70 Hz. Long-range couplings to 1H are sufficient to allow indirect observation of rhodium using heteronuclear correlation (fig. 2).
Properties of 103Rh
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Spin | 1/2 |
| Natural abundance | 100% |
| Chemical shift range | 12493 ppm, from -10257 to 2236 |
| Frequency ratio (Ξ) | 3.186447% (alt. 3.16%) |
| Reference compound | Rh(acac)3 (sat.) in CDCl3 |
| Linewidth of reference | 14 Hz |
| T1 of reference | 1 s |
| Receptivity rel. to 1H at natural abundance | 3.17 × 10-5 |
| Receptivity rel. to 1H when enriched | 3.17 × 10-5 |
| Receptivity rel. to 13C at natural abundance | 0.186 |
| Receptivity rel. to 13C when enriched | 0.186 |
Safety note
Some of the materials mentioned here are very dangerous. Ask a qualified chemist for advice before handling them. Qualified chemists should check the relevant safety literature before handling or giving advice about unfamiliar substances. NMR solvents are toxic and most are flammable. Specifically, rhodium salts are toxic: wear protective gloves.
References
- W. von Philipsborn, Pure Appl. Chem., 58, 513 (1986).
- B. E. Mann In Transition Metal Nuclear Magnetic Resonance, Pregosin PS (ed.). Elsevier: Amsterdam, 1991; 177
- W. von Philipsborn, Chem. Soc. Rev., 28, 95 (1999).
- J. M. Ernsting, S. Gaemers and C. J. Elsevier, "103Rh NMR spectroscopy and its application to rhodium chemistry", Magn. Reson. Chem, 42, 721–736 (2004).