(77Se) Selenium NMR
Use our NMR service that provides 77Se NMR and many other NMR techniques.
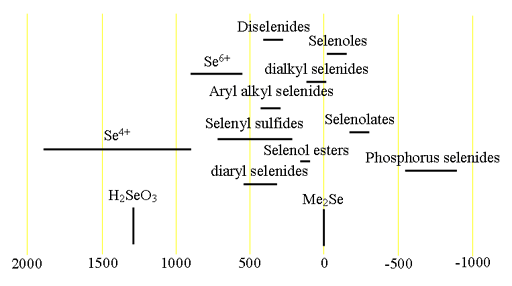
77Selenium (77Se) is a low sensitivity spin ½ nucleus that yields narrow lines over a very wide chemical shift range. Each type of selenium compound has its characteristic chemical shift range (fig. 1).
Fig. 1. Chemical shift ranges for selenium NMR
Selenium NMR (fig. 2) is used extensively in the study of organoselenium compounds such as selenoxanthenone (fig. 3) and for studies of selenium binding to proteins.
Fig. 2. Proton decoupled 77Se-NMR spectrum of selenoxanthenone (0.1 M) in CDCl3
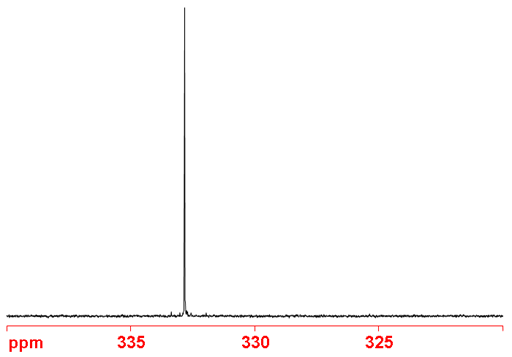
Fig. 3. Molecular structure of selenoxanthenone
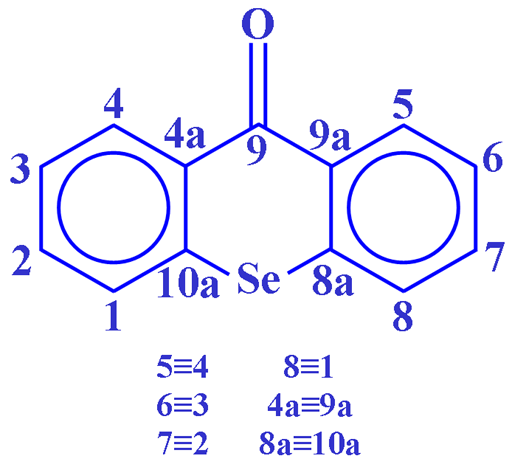
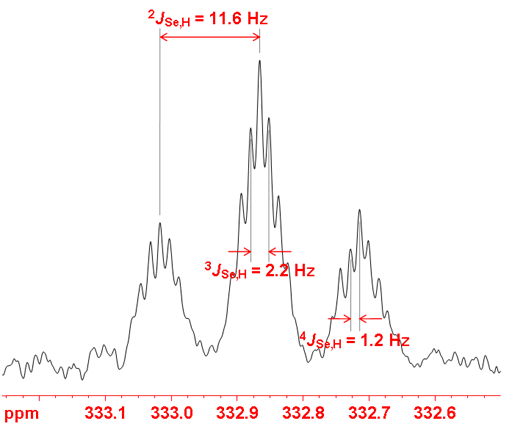
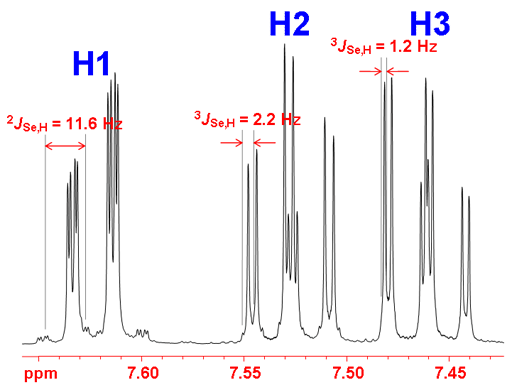
Selenium often shows couplings to other nuclei, 1H, 13C, 15N, 19F, 31P, etc. It also displays homonuclear couplings with three-bond selenium-selenium couplings between 10 and 100 Hz that depend on stereochemistry. Selenium couplings to protons can be removed by decoupling as in fig. 2. The coupled spectrum of selenoxanthenone (fig. 4) shows a three bond coupling to H1 (3JSe,H) of 11.6 Hz, four bond coupling to H2 (4JSe,H) of 2.2 Hz and five bond to H3 (5JSe,H) of 1.2 Hz. A six bond coupling was not observed although it is expected to be about 0.5 Hz.
Fig. 4. 77Se-NMR spectrum of selenoxanthenone (0.1 M) in CDCl3 showing proton coupling
The selenium couplings are also observed as satellites in the proton spectrum (fig. 5). They only appear as satellites because the abundance of 77Se is only 7.63%.
Fig. 5. 1H-NMR spectrum of selenoxanthenone (0.1 M) in CDCl3 showing 77Se coupling
13C coupling is manifested as small satellite signals in the 77Se spectrum (fig. 6). Here couplings up to three bonds are observed. One bond coupling constants are in the region of 100 Hz, 2 and 3 bond couplings range from 5 to 35 Hz and longer range couplings are less than 3 Hz.
Fig. 6. Proton decoupled 77Se-NMR spectrum of selenoxanthenone (0.1 M) in CDCl3 showing satellites arising from 13C coupling

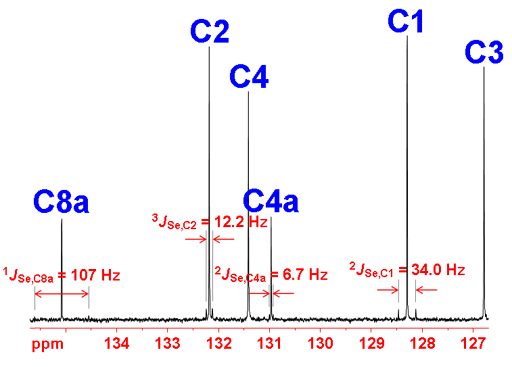
Selenium carbon coupling is also seen as satellite signals in the 13C-NMR spectrum (fig. 7).
Fig. 7. Proton decoupled 13C-NMR spectrum of selenoxanthenone (0.1 M) in CDCl3 showing satellites arising from 77Se coupling
Properties of 77Se
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Spin | 1/2 |
| Natural abundance | 7.63% |
| Chemical shift range | 3000 ppm, from -1000 to 2000 |
| Frequency ratio (Ξ) | 19.071513% |
| Reference compound | Me2Se |
| Linewidth of reference | ~0.5 Hz |
| T1 of reference | ~30 s |
| Receptivity rel. to 1H at natural abundance | 5.37 × 10-4 |
| Receptivity rel. to 1H when enriched | 7.04 × 10-3 |
| Receptivity rel. to 13C at natural abundance | 3.15 |
| Receptivity rel. to 13C when enriched | 41.3 |
Safety note
Some of the materials mentioned here are very dangerous. Ask a qualified chemist for advice before handling them. Qualified chemists should check the relevant safety literature before handling or giving advice about unfamiliar substances. NMR solvents are toxic and most are flammable. Specifically, selenium compounds are toxic or very toxic, work in a hood and use appropriate gloves and protective clothing. Latex gloves are insufficient protection against organoselenium compounds.
References
- M. Lardon, "Selenium and proton nuclear magnetic resonance measurements on organic selenium compounds", J. Am. Chem. Soc., 92, 5063-5066 (1970).
- W. McFarlane and D. S. Rycroft, "Signs of nuclear spin-spin coupling constants involving selenium. Effect of electron lone pairs", J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun., 10-11 (1973).
- S. Gronowitz, I. Johnson and A. B. Hornfeldt, "Selenium-77 NMR studies of organoselenium compounds. I. Selenium-77 NMR parameters of monosubstituted selenophenes", Chem. Script., 8, 8-14 (1975).
- L. Christiaens, J. L. Piette, L. Laitem, M. Baiwir, J. Denoel and G. Llabres, "Selenium-77 NMR of organoselenium compounds", Org. Magn. Reson., 8, 354-356 (1976).
- A. Fredga, S. Gronowitz and A. B. Hornfeldt, "Selenium-77 NMR studies of organoselenium compounds. IV. Benzyl- and arylseneinic acids", Chem. Script., 11, 37-38 (1977).
- G. A. Kalabin, D. F. Kushnarev and V. M. Tschmutova, "Proton, carbon-13, and selenium-77 NMR spectra of substituted selenoanisoles", Org. Magn. Reson., 12, 598-604 (1979).
- R. Keat, D. S. Rycroft and D. G. Thompson, "Selenium-77 chemical shifts of cylodiphosphazene selenides", Org. Magn. Reson., 12, 391-392 (1979).
- B. Kohne, W. Lohner, K. Praefcke, H. J. Jakobsen and B. Villadsen, "Spectroscopic investigations XVII. 77Se and 125Te NMR resonances of some selenol and tellurol esters", J. Organometal. Chem., 166, 373-377 (1979).
- G. Llabres, M. Baiwir, J. L. Piette and L. Christiaens, "Selenium-77, carbon-13 and proton NMR investiagation on ortho-carbonyl benzeneselenyl derivatives", Org. Magn. Reson., 15, 152-154 (1981).
- N. V. Onyamboko, M. Renson, S. Chapelle and P. Granger, "Carbon-13 and Selenium-77 spectra of thienoisoselenazoles, selenoloisothiazoles, selnoloisoselnazoles, and thienoisothiazoles", Org. Magn. Reson., 19, 74-77 (1982).
- D. F. Kushnarev, G. A. Kalabin, R. A. Kyandzhetsian and N. N. Magdesieva, "NMR spectroscopy of organic compounds of selenium and tellurium. X. Chemical shifts of selenium-77 in selenonium ylides", Zh, Org. Khim., 18, 119-124 (1982).
- M. Baiwir, G. Llabres, L. Christiaens and J. L. Piette, "NMR studies of the chalcogen analogs of benzofuran. IV. Proton, carbon-13 and selenium-77 magnetic resonance in nitrobenzo[b]selenophenes", Org. Magn. Reson., 18, 33-37 (1982).
- N. P. Luthram R. B. Dunlap and J. D. Odom "Selenium-77 NMR studies of organic selenyl sulfides", J. Magn. Reson., 46, 152-157 (1982).
- I. Johannsen and H. Eggert, "Selenium-77 NMR. Observation of 3JSe-Se coupling allowing cis/trans isomer assignments in substituted tertaselenfulvalenses", J. Am. Chem. Soc., 106, 1240-1243 (1984).
- H. Duddeck, P. Wagner and S. Gegner, "Dynamic 77Se NMR of phenylselenyl cyclohexane derivatives", Tetrahed. Lett., 26, 1205-1208 (1985).
- H. Eggert, O. Nielson and L. Henriksen, "Selenium-77 NMR. Application of JSe-Se to the analysis of dialkyl selenides", J. Am. Chem. Soc., 108, 1725-1730 (1986).
- I. Johannsen, L. Henrikson and H. Eggert, "Selenium-77 NMR. 2. The basis for application of JSe-Se and JSe-H in structure assignments of mono-, di-, and triseleno-substituted alkenes", J. Org. Chem., 51, 1657-1663 (1986).
- K. S. Tan, A. P. Arnold and D. L. Rabenstein, "Selenium-77 nuclear magnetic resonance studies of selenols, diselenides, and selenyl sulfides", Can. J. Chem., 66, 54-60 (1988).
- B. Wrackmeyer, B. Distler, S. Gerstmann and M. Herberhold, "Nitrogen-15 and Selenium-77 nuclear magnetic resonance study of selenium diimides and aminoselenanes", Z. Naturfors. B, 48, 1307-14 (1993).
- B. W. Tattershall and E. L. Sandham, "Interdependence of phosphorus-31 selenium-77 NMR coupling constants in bicyclic phosphorus selenide compounds", J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans., 1834-1840 (2001).