(V) Vanadium NMR
Use our NMR service that provides V NMR and many other NMR techniques.
Vanadium (V) has two NMR active nuclei, 50V and 51V, with a very wide chemical shift range (fig. 1). Both nuclei are quadrupolar and therefore yield relatively broad signals in small molecules and signals, too broad to be observed with a high-resolution NMR spectrometer, in large molecules. 51V is the nucleus of choice because it is by far the more sensitive and yields much narrower lines although this is only relative and 51V signals are quite broad (fig. 2). Vanadium NMR is used in the study of small vanadium complexes and vanadium binding in solution.
Fig. 1. Chemical shift ranges for vanadium NMR

Fig. 2. Comparison of 50V and 51V for VOCl3 (neat). 51V yields much greater sensitivity and much narrower signals.

Each type of vanadium compound has its characteristic chemical shift range (fig. 1). The NMR of Vanadium can be observed in its (-I), (I), and (V) oxidation states however, V(0), (II) and (IV) are paramagnetic and cannot be observed in high resolution NMR.
50Vanadium NMR
50V (fig. 3) is much less sensitive and yields much broader signals than 51V so is not the nucleus of choice.
Fig. 3. 50V-NMR spectrum of neat VOCl3
Properties of 50V
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Spin | 6 |
| Natural abundance | 0.250% |
| Chemical shift range | 1900 ppm, from -1900 to 0 |
| Frequency ratio (Ξ) | 9.970309% |
| Reference compound | VOCl3 (90%) in C6D6* |
| Linewidth of reference | 68 Hz |
| T1 of reference | 0.005 s |
| Receptivity rel. to 1H at natural abundance | 1.39 × 10-4 |
| Receptivity rel. to 1H when enriched | 0.0556 |
| Receptivity rel. to 13C at natural abundance | 0.818 |
| Receptivity rel. to 13C when enriched | 327 |
| Linewidth parameter | 17 fm4 |
*Note that pure VOCl3 resonates at 2 ppm in the 50V-NMR spectrum.
51Vanadium NMR
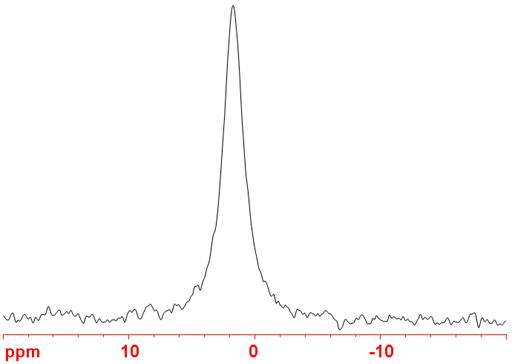
51V preferred as an NMR nucleus over 50V because it is much more sensitive and yields shaper signals. 51V yields somewhat broad lines in small symmetric molecules (fig. 4) but its signals become wider with increasing size of the complex and too broad to observe with a high-resolution NMR spectrometer for medium sized complexes. 51V NMR is used in the study of small vanadium complexes and vanadium binding in solution.
Fig. 4. 51V-NMR spectrum of neat VOCl3

Properties of 51V
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Spin | 7/2 |
| Natural abundance | 99.750% |
| Chemical shift range | 1900 ppm, from -1900 to 0 |
| Frequency ratio (Ξ) | 26.302948% |
| Reference compound | VOCl3 (90%) in C6D6 |
| Linewidth of reference | 21 Hz |
| T1 of reference | 0.0203 s |
| Receptivity rel. to 1H at natural abundance | 0.383 |
| Receptivity rel. to 1H when enriched | 0.384 |
| Receptivity rel. to 13C at natural abundance | 2250 |
| Receptivity rel. to 13C when enriched | 2256 |
| Linewidth parameter | 3.7 fm4 |
*Note that pure VOCl3 resonates at 2 ppm in the 51V-NMR spectrum.
Safety note
Some of the materials mentioned here are very dangerous. Ask a qualified chemist for advice before handling them. Qualified chemists should check the relevant safety literature before handling or giving advice about unfamiliar substances. NMR solvents are toxic and most are flammable. Specifically, VOCl3 is toxic and reacts with moist air to give toxic fumes (HCl): wear gloves, work under nitrogen in a hood. Vanadium salts are toxic: wear gloves. 50V is very slightly radioactive but is not considered a radiation hazard, at least at natural abundance.