(61Ni) Nickel NMR
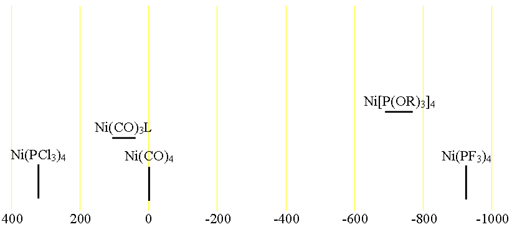
61Nickel (61Ni) is a low sensitivity nucleus with a low natural abundance that yields somewhat broad lines even in symmetric environments and very broad lines for slightly larger complexes over a very wide chemical shift range. 61Ni is a spin 3/2 nucleus and is therefore quadrupolar. As a result, the signal width increases with asymmetry of the environment. The most common oxidation state of nickel salts is Ni(II). However, this oxidation state is paramagnetic in the square-planar form so cannot be observed on a high resolution NMR spectrometer but could be observed in principle for complexes that take on the pure diamagnetic tetrahedral form. 61Ni NMR is most commonly observed for Ni(0) and is usually used for the study of Ni(0) complexes. Each type of nickel compound has its characteristic chemical shift (fig. 1). One bond coupling constants to 31P of 400 to 470 Hz are observed and two bond couplings to 19F in Ni(PF3)4 are 28 Hz.
Fig. 1. Chemical shift ranges for nickel NMR
We do not have experience of 61Ni NMR in our laboratory but could provide the service if given an appropriate sample.
Properties of 61Ni
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Spin | 3/2 |
| Natural abundance | 1.1399% |
| Chemical shift range | 1200 ppm, from -930 to 270 |
| Frequency ratio (Ξ) | 8.936051% |
| Reference compound | Ni(CO)4 80% in C6D6 |
| Linewidth of reference | 7 Hz |
| T1 of reference | 0.05 s |
| Receptivity rel. to 1H at natural abundance | 4.09 × 10-5 |
| Receptivity rel. to 1H when enriched | 0.0359 |
| Receptivity rel. to 13C at natural abundance | 0.240 |
| Receptivity rel. to 13C when enriched | 21.1 |
| Linewidth parameter | 350 fm4 |
References
- N. Hao, M. J. McGlinchey, B. G. Sayer and G. J. Schrobilgen, "A 61Ni NMR Study of Some d10 Nickel Complexes", J. Magn. Reson., 46, 158-162 (1982).
Safety note
Some of the materials mentioned here are very dangerous. Ask a qualified chemist for advice before handling them. Qualified chemists should check the relevant safety literature before handling or giving advice about unfamiliar substances. NMR solvents are toxic and most are flammable. Specifically, nickel salts are toxic and Ni(CO)4 is extremely toxic, work in a hood with appropriate gloves.