(75As) Arsenic NMR
Use our NMR service that provides 75As NMR and many other NMR techniques.
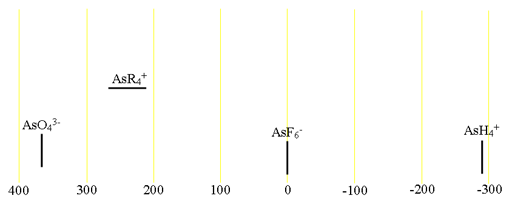
75Arsenic (75As) is the only NMR active nucleus of arsenic. It is a moderate sensitivity quadrupolar spin 3/2 nucleus that yields broad lines even for small molecules in symmetric environments (fig. 1) over a wide chemical shift range. For larger and asymmetric molecules, the signals become too broad to observe with a high-resolution NMR spectrometer. Arsenic NMR is used for the study of small arsenic ions and, using their relaxation properties, their interaction with other molecules. Each type of arsenic compound has its own chemical chemical shift range (fig. 2).
Fig. 1. 75As-NMR spectrum of Na3AsO4 in concentrated NaOD
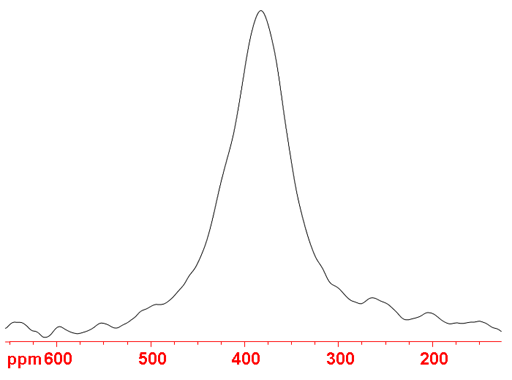
Fig. 2. Chemical shift ranges for arsenic NMR
An interesting example is (fig. 1) sodium arsenate (Na3AsO4) that yields signals too broad to observe with a high resolution spectrometer at neutral pH but in concentrated alkali solutions yields a broad but observable 4 kHz wide signal. This is due to the formation of the asymmetric HAsO42- anion at neutral pH.
Heteronuclear coupling of 930 Hz is observed to 19F in AsF6-.
Properties of 75As
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Spin | 3/2 |
| Natural abundance | 100% |
| Chemical shift range | 660 ppm, from -291 to 369 |
| Frequency ratio (Ξ) | 17.122614% |
| Reference compound | 0.5 M NaAsF6 in CD3CN |
| Linewidth of reference | 90 Hz |
| T1 of reference | 0.002 s |
| Receptivity rel. to 1H at natural abundance | 0.0254 |
| Receptivity rel. to 1H when enriched | 0.0254 |
| Receptivity rel. to 13C at natural abundance | 149 |
| Receptivity rel. to 13C when enriched | 149 |
| Linewidth parameter | 1300 fm4 |
Safety note
Some of the materials mentioned here are very dangerous. Ask a qualified chemist for advice before handling them. Qualified chemists should check the relevant safety literature before handling or giving advice about unfamiliar substances. NMR solvents are toxic and most are flammable. Specifically, arsenic compounds are very toxic.
References
- G. Balimann and P. S. Pregosin, "Arsenic-75 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance. A Strudy of Some Arsenic Salts", J. Magn. Reson., 26, 283-289 (1977).
- M. J. Collins, U. R. K. Rao and G. J. Schrobilgen, "75Arsenic NMR study of [As(OTeF5)6]- in Solution", J. Magn. Reson., 61, 137-140 (1985).
- C. F. G. C. Geraldes, M. E. Saraiva and B. A. Diss, "Arsenic-75 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance: Study of the Interaction of Arsenate with Various Molecules of Biological Interest", J. Inorg. Biochem., 46, 99-108 (1992).