(17O) Oxygen NMR
Oxygen has one naturally occurring NMR active nucleus, 17O. It has a spin of 5/2 and is therefore quadrupolar, yielding broad signals even for the smallest of molecules that become too broad to observe in a high resolution spectrometer even for medium sized molecules. The isotope 17O has a very low natural abundance of 0.038% combined with a relatively low receptivity and so is only observable for high concentrations (at least molar) or when enriched (very expensive, currently over $1000/mL of H217O, never mind anything more complicated). 17O has a very wide chemical shift range which for small molecules partially compensates for its broad signals. Each type of signal has a characteristic chemical shift range (figs. 1, 2).
Fig. 1. Chemical shift ranges for 17O NMR
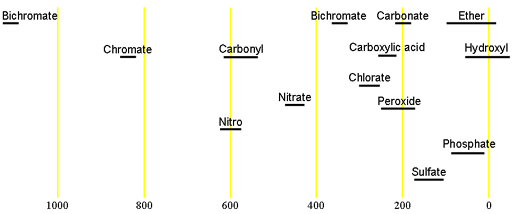
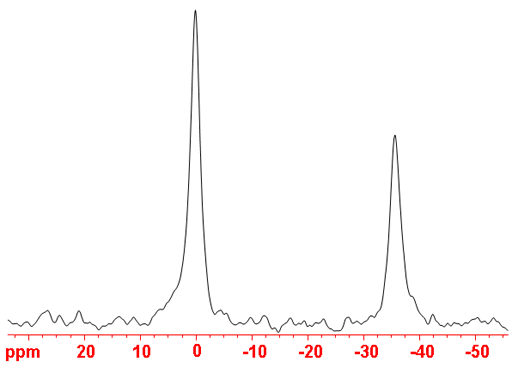
Fig. 2. 17O-NMR spectrum of D2O (peak on the left) and CD3OD (right)
Properties of 17O
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Spin | 5/2 |
| Natural abundance | 0.038% |
| Chemical shift range | 1160 ppm, from -40 to 1120 |
| Frequency ratio (Ξ) | 13.556457% |
| Reference compound | D2O |
| Linewidth of reference | 69 Hz |
| T1 of reference | 0.02 s |
| Receptivity rel. to 1H at natural abundance | 1.11 × 10-5 |
| Receptivity rel. to 1H when enriched | 0.0291 |
| Receptivity rel. to 13C at natural abundance | 0.0650 |
| Receptivity rel. to 13C when enriched | 171 |
| Linewidth parameter | 2.1 fm4 |
Safety note
Some of the materials mentioned here are very dangerous. Ask a qualified chemist for advice before handling them. Qualified chemists should check the relevant safety literature before handling or giving advice about unfamiliar substances. NMR solvents are toxic and most are flammable. Specifically, D2O is toxic.